Background
Django, with its built-in ORM (Object Relational Mapping) and QuerySet, provides users an easy way to deal with relational database. You do not need to know SQL commands to perform database queries. In addition, django-debug-toolbar is available for your to inspect how the QuerySet are transformed into SQL commands and how much time each query command takes, to further improve the performance.
To me, SQL queries are still useful for data processing and analyzing when working with relational databases. This post revisits some of the core SQL commands, thought there are many intuitive tools available for creating and managing database schemas and perform analyses, e.g., MySQL Workbench, SQL Sever Management Studio, Sequel Pro.
Core SQL Commands
The following SQL commands were written and tested with MySQL Workbench 6.2.
- Create a database
CREATE DATABASE testsql;
- Change to a database
USE testsql;
- Create a table with PK
CREATE TABLE Customer(
id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
firstName VARCHAR(50),
lastName VARCHAR(50),
age INT,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
CREATE TABLE product(
productId INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
productName VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
price DECIMAL(10,2) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(productID)
);
CREATE TABLE orders(
orderId INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
customerID INT NOT NULL,
productID INT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (orderId)
);
- Add FK to a table
ALTER TABLE orders
ADD FOREIGN KEY (customerID) REFERENCES Customer(id) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT,
ADD FOREIGN KEY (productID) REFERENCES product(productID) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT;
- Insert records to a table
INSERT INTO Customer(firstName,lastName,age) VALUES ('Tandy', 'Tan', 20);
INSERT INTO Customer(firstName,lastName,age) VALUES ('Tandy', 'Wan1', 20);
INSERT INTO Customer(firstName,lastName,age) VALUES ('Tandy', 'Wan2', 20);
INSERT INTO Customer(firstName,lastName,age) VALUES ('Tandy', 'Wan3', 20);
INSERT INTO Customer(firstName,lastName,age) VALUES ('Tandy', 'Wan4', 20);
INSERT INTO Customer(firstName,lastName,age) VALUES ('Jerramy', 'Micheale', 36);
INSERT INTO Customer(firstName,lastName,age) VALUES ('Tony', 'Fadile', 18);
INSERT INTO Customer(firstName,lastName,age) VALUES ('Jhon', 'Smith', 44);
INSERT INTO Customer(firstName,lastName,age) VALUES ('Jhon', 'Smith', 44);
INSERT INTO Customer(firstName,lastName,age) VALUES ('Jhon', 'Smith', 44);
INSERT INTO Customer(firstName,lastName,age) VALUES ('Marien', 'Clack', 22);
INSERT INTO testsql.product(productName, price) VALUES ('Baseball', 19.99);
INSERT INTO testsql.product(productName, price) VALUES ('Bat', 195.99);
INSERT INTO orders (customerID, productID) VALUES(6,2);
INSERT INTO orders (customerID, productID) VALUES(12,1);
INSERT INTO orders (customerID, productID) VALUES(16,2);
- View the table with all fields
SELECT * FROM testsql.Customer;
- View the distinct values from a table field
SELECT DISTINCT firstName FROM testsql.Customer;
- Select objects using like keyword and % or _ wildcard
-
%:0,1or more characters; -
_:1(single) character;
SELECT * FROM testsql.Customer
WHERE firstName='Tandy'
AND lastName LIKE 'Wan_';
LIKE Operator |
Description |
|---|---|
WHERE lastName LIKE 'a%' |
Finds any values that starts with “a” |
WHERE lastName LIKE '%a' |
Finds any values that ends with “a” |
WHERE lastName LIKE '%or%' |
Finds any values that have “or” in any position |
WHERE lastName LIKE '_r%' |
Finds any values that have “r” in the second position |
WHERE lastName LIKE 'a_%_%' |
Finds any values that starts with “a” and are at least 3 characters in length |
WHERE ContactName LIKE 'a%o' |
Finds any values that starts with “a” and ends with “o” |
- update a filed of a table
UPDATE testsql.Customer
SET age=28
WHERE id=6;
The following only works when Safe Update is disabled and without an pk in the WHERE clause
UPDATE testsql.Customer
SET age=44
WHERE firstName='Tandy'
AND lastName='Tan';
- Delete records from a table
DELETE FROM testsql.Customer
WHERE firstName='Tandy'
AND lastName LIKE "Wan_";
- Add a column/new field to a table without/with default value
ALTER TABLE testsql.Customer
ADD city VARCHAR(50);
ALTER TABLE orders
ADD orderDate datetime DEFAULT now();
- Add a column with default value
ALTER TABLE testsql.Customer
ADD city VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT 'Montreal';
- Delete a column/field from a table
ALTER TABLE testsql.Customer
DROP city;
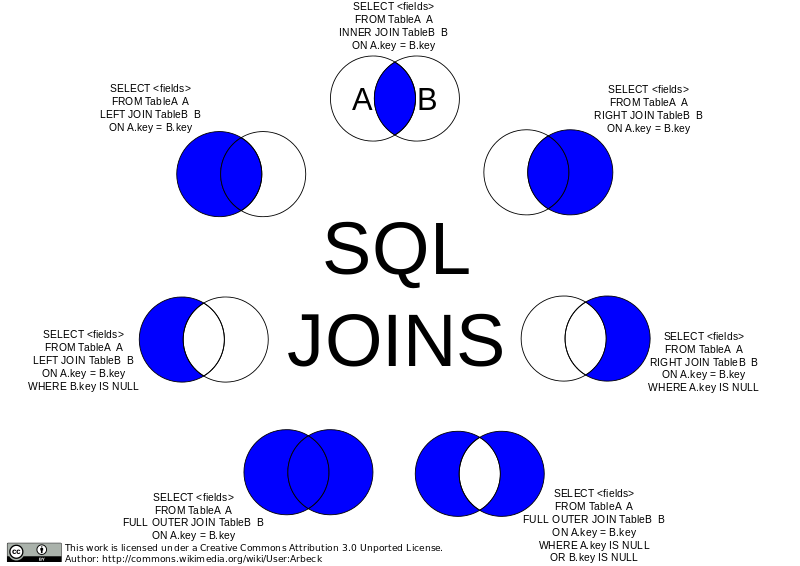
- Join tables and aliases
SELECT o.orderDate, p.productName, p.price, c.*
FROM orders as o
INNER JOIN product as p ON o.productID=p.productID
INNER JOIN Customer AS c ON o.customerID=c.id;
- Functions
SELECT SUM(p.price) as TOTAL
from orders AS o
INNER JOIN product AS p on o.productID=p.productID;
- Group by
SELECT c.lastName, p.productName, sum(p.price) AS TOTAL
from orders AS o
INNER JOIN product AS p on o.productID=p.productID
INNER JOIN Customer c on o.customerID=c.id
GROUP BY c.lastName, p.productName;
SELECT c.city, sum(p.price) TOTAL
from orders o
INNER JOIN product p on o.productID=p.productID
INNER JOIN Customer c on o.customerID=c.id
GROUP BY c.city;